Credit risk analysis techniques help banks assess borrowers' repayment ability and likelihood of default, minimizing risks and financial losses. This blog covers traditional and modern methods, emphasizing the need for robust, scalable frameworks amid rising credit lending volumes. By adopting both approaches, banks can enhance compliance, stability, and competitiveness.
Credit risk analysis techniques are the quantitative tools banks use to evaluate a borrower’s ability to repay a loan and determine the likelihood of default. In the current economic landscape of late 2025, with businesses and consumers adapting to a period of sustained higher interest rates, the precision of these techniques is more critical than ever.
Throughout 2024 and 2025, default rates, particularly in speculative-grade debt, have trended upwards as predicted by firms like S&P Global. As we look toward 2026, the focus sharpens on deploying robust and dynamic risk assessment frameworks to navigate this challenging environment.
This guide explores the key traditional and modern techniques for analyzing credit risk, providing a roadmap for maintaining a healthy and competitive lending portfolio today.
Traditional Credit Risk Analysis Techniques
These foundational methods have long been the bedrock of credit risk assessment, providing essential, explainable insights.
1. Credit Scoring
Credit scoring is a widely used statistical method to assess the credit risk of individual borrowers. Credit reporting agencies like Experian and Equifax provide numerical scores based on several factors:
- Payment History
The borrower’s track record of on-time payments and any past delinquencies. - Credit Utilization
The ratio of current credit balances to total available credit limits. A lower ratio is generally better. - Length of Credit History
A longer history of responsible credit management is typically viewed favorably. - Types of Credit Used
A mix of different credit types (e.g., credit cards, installment loans) can indicate responsible credit management. - New Credit Inquiries
Recent credit inquiries and newly opened accounts, as frequent applications can signal risk.
2. Financial Statement Analysis
For corporate borrowers, banks perform a deep analysis of key financial statements. This involves evaluating key financial ratios, with a heightened focus on specific metrics in the current climate:
- Liquidity Ratios
Measures a company’s ability to meet its short-term obligations (e.g., current ratio, quick ratio). - Leverage Ratios
Evaluates the extent to which a company uses debt to finance its assets (e.g., debt-to-equity ratio). - Cash Flow Analysis
Examines cash inflows and outflows. In a high-interest-rate environment, this is arguably the most critical metric, as it directly indicates a company’s ability to service its more expensive debt.
Modern Credit Risk Analysis Techniques
Modern techniques leverage advanced technology and data for more accurate and dynamic risk assessments, which are essential for navigating today’s volatility.
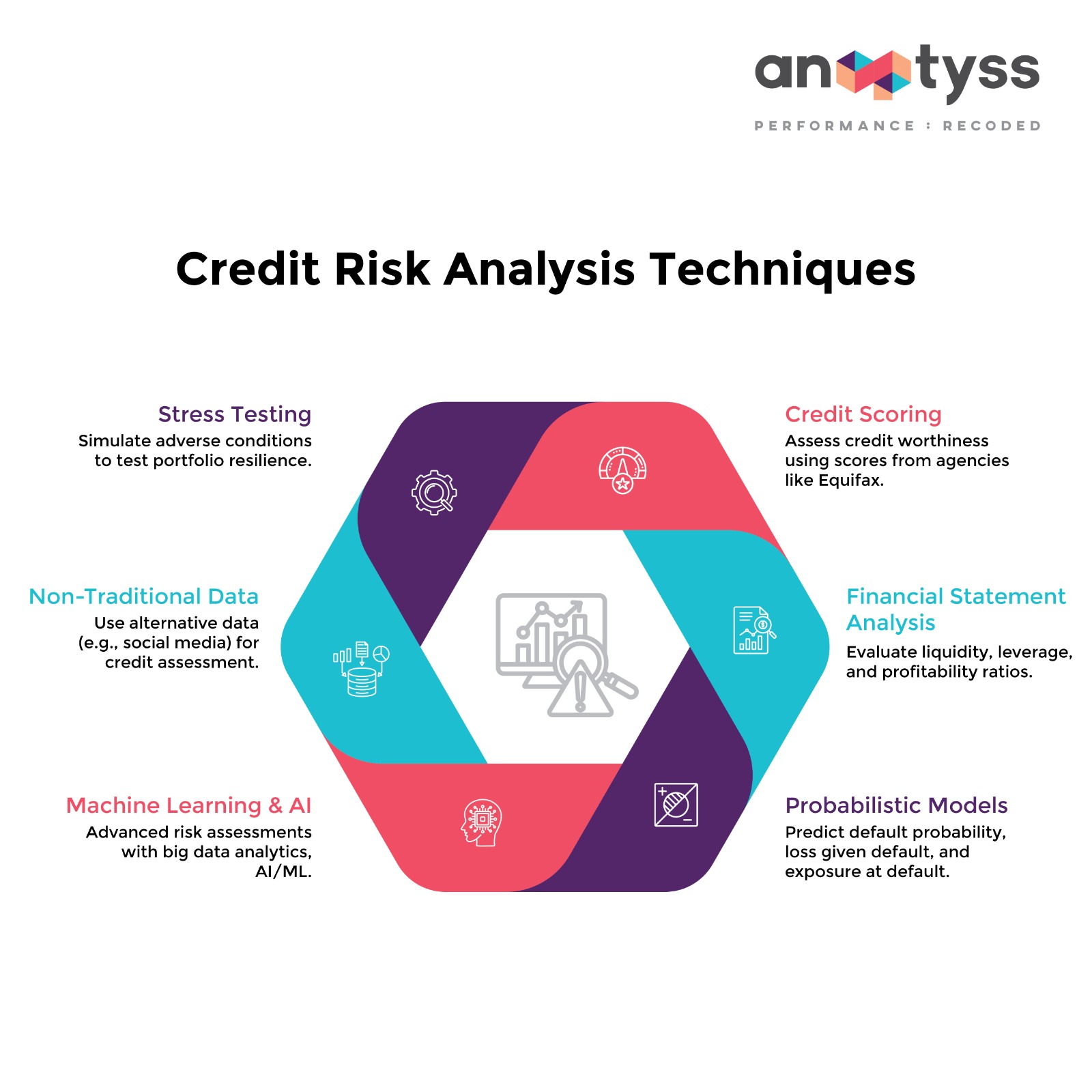
3. Probabilistic Models
These models use historical data and statistical analysis to forecast the likelihood of future outcomes. Key metrics include:
- Probability of Default (PD)
Estimates the likelihood that a borrower will default within a specific time horizon. - Loss Given Default (LGD)
Measures the expected financial loss if a borrower defaults on a loan. - Exposure at Default (EAD)
Represents the total value a bank is exposed to at the time a borrower defaults.
4. Stress Testing
Stress testing simulates extreme but plausible adverse economic conditions. In the context of 2025, these simulations have evolved to model scenarios like prolonged inflation, specific geopolitical supply chain disruptions, and sudden liquidity shocks. For a deeper analysis, explore the role and importance of stress testing.
5. Integration of Non-Traditional Data
To gain a more holistic view of a borrower’s creditworthiness, modern analysis incorporates alternative data sources beyond traditional credit reports. This can include utility payments, rental history, and online transaction data, which is especially useful for assessing individuals with limited credit histories.
6. Machine Learning and AI
AI and machine learning are now central to advanced credit risk analysis. Beyond simply processing vast amounts of data, the focus has shifted to new applications and challenges:
- Predictive Analytics — AI models continuously update risk profiles based on real-time data, enabling proactive interventions before a borrower gets into trouble. Learn more about how AI is reshaping credit risk analytics.
- Generative AI — Banks are now using Generative AI to create high-quality synthetic data, which helps train and validate risk models without compromising customer privacy.
- Model Risk Management (MRM) — As AI models become more complex, the discipline of MRM has become critical. Banks must have robust processes to validate, monitor, and govern these models to ensure they are fair, accurate, and compliant. Explore more about what Model Risk Management (MRM) is.
For more strategies on this topic, you can refer to our white paper on Credit Portfolio Management In an Era of Fluctuating Interest Rates.
Choosing the Right Technique: A Quick Comparison
- Traditional Techniques — Best for foundational analysis, regulatory compliance, and assessing borrowers with established credit histories. They are transparent and well-understood but can be slow and may overlook nuances in alternative data.
- Modern Techniques — Ideal for enhancing accuracy, processing large and complex datasets, and assessing borrowers with thin credit files. They provide predictive insights but can be complex to implement and may require significant investment in technology and talent.
A hybrid approach that combines the reliability of traditional methods with the predictive power of modern technology often yields the best results.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- How has the economic climate of 2025 impacted credit risk analysis?
The sustained higher interest rates of 2024-2025 have increased the cost of borrowing, placing more stress on both corporate and consumer debt. This has made forward-looking techniques like stress testing and real-time AI-powered monitoring more critical than ever. There is a greater focus on cash flow analysis and less reliance on historical data that was captured in a low-interest-rate environment. - What is the most common credit risk analysis technique?
For individual borrowers, credit scoring remains the most common and fundamental technique. For corporate borrowers, financial statement analysis is the standard starting point. - How has AI changed credit risk analysis?
AI has revolutionized credit risk analysis by enabling banks to process massive, diverse datasets in real-time. It has significantly improved the accuracy of default prediction, automated manual processes, and allowed for the inclusion of alternative data, leading to more inclusive and precise lending decisions.
Conclusion
Effective credit risk management in the current 2025 economic climate requires a dynamic and adaptive approach. While traditional techniques provide an essential foundation of stability and explainability, the integration of modern, technology-driven analysis is crucial for navigating today’s volatility. By implementing a hybrid strategy, financial institutions can make more accurate lending decisions, proactively manage their portfolios, and build a resilient framework for the challenges of 2026 and beyond.
For more information, please connect with us at info@anaptyss.com.


















