In this blog, we delve into the Financial Action Task Force (FATF), focusing on its evolving standards for combating money laundering and terrorist financing. We summarize the key FATF Recommendations, their impact, and how Anaptyss helps institutions comply with these standards effectively.
Financial Action Task Force (FATF) is an intergovernmental policy & standard-setting body of the U.S. Department of the Treasury dedicated to countering terror financing and money laundering activities.
The FATF Recommendations set an international standard that countries need to implement through measures adapted to their legal, administrative, and operational frameworks and financial systems.
It provides a comprehensive and coherent framework for measures that countries should take to combat money laundering, financing terrorism, and financing proliferation of the weapons of mass destruction.
Evolution of FATF Standards
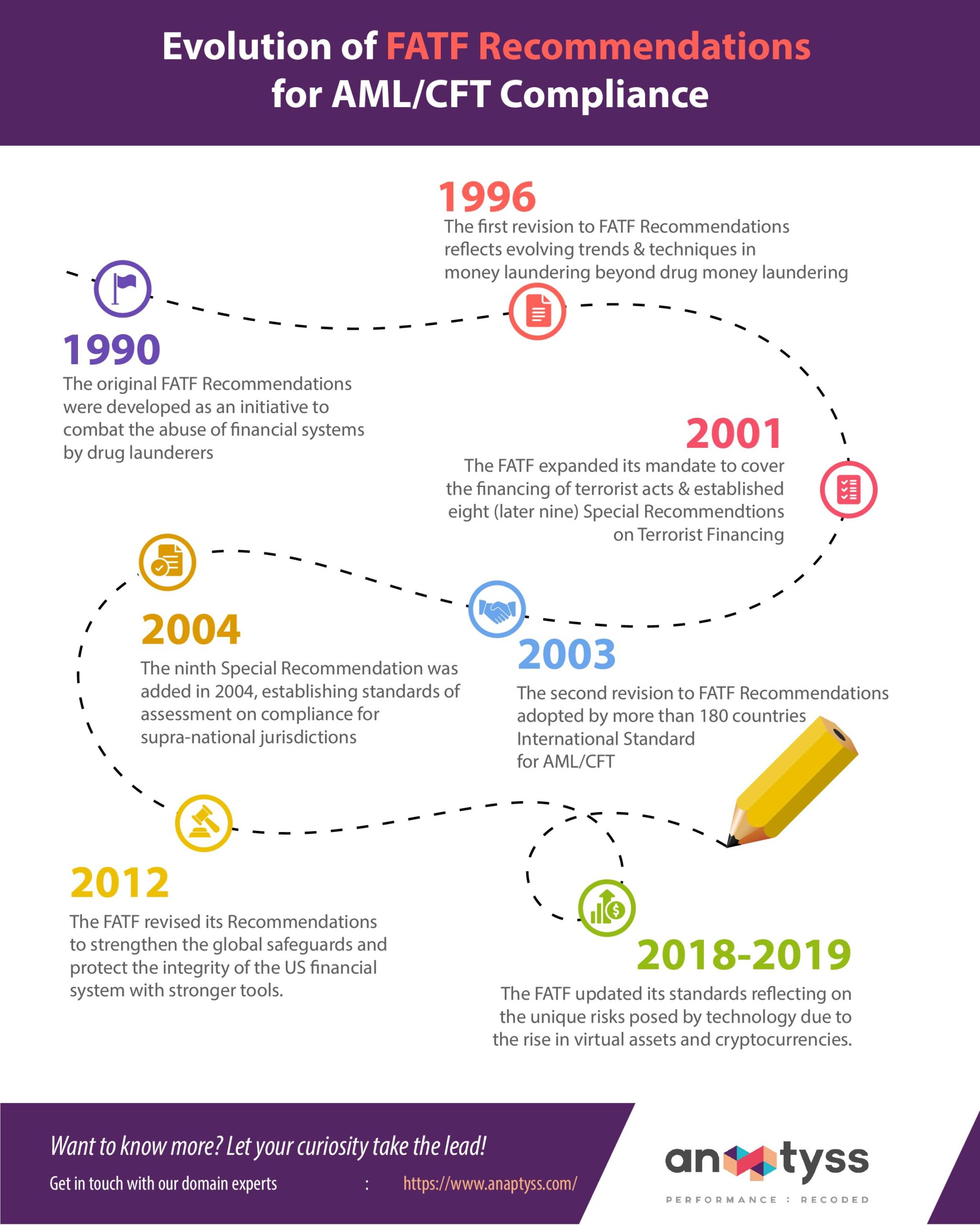
FATF 40+9 Recommendations provide a basic framework to detect, prevent, and suppress the financing of terrorism and terrorist acts. It sets international standards for combating terrorist financing and money laundering (ML). Here’s a summary of the evolution and history of the FATF Recommendations:
- The original FATF Recommendations were developed in 1990 as an initiative to combat the abuse of financial systems by drug money launderers.
- In 1996, the Recommendations were revised for the first time to reflect evolving trends and techniques in money laundering and to expand their scope significantly beyond drug money laundering.
- In October 2001, the FATF expanded its mandate to cover the financing of terrorist acts and organizations and took the important step of establishing eight (later nine) Special Recommendations on Terrorist Financing.
- The FATF Recommendations were revised for the second time in 2003 and have been adopted by more than 180 countries with specific recommendations and are widely recognized as the International Standard for Anti-Money Laundering and the Financing of Terrorism (AML/CFT) Amendments to address new and emerging threats and to clarify and strengthen many existing obligations while maintaining the necessary stability and discipline of recommendations.
- The ninth FATF recommendation was added in 2004, establishing standards of assessment on compliance for supra-national jurisdictions.
- After conducting a major review of the recommendations, FATF revised them in 2012 to strengthen the global safeguards and protect the integrity of the US financial system with robust tools to help the government take stringent actions against financial crime.
- In 2012, the additional eight recommendations were also incorporated with the 40 recommendations with special emphasis on the predicate offenses for moving the illicit proceeds.
- In October 2018 and June 2019, FATF updated its standards reflecting on the unique risks posed by technology due to the rise in virtual assets and cryptocurrencies.
FATF standards have also been revised to strengthen requirements for higher-risk situations and allow countries to take a more targeted approach in areas where risks remain high or where enforcement could be strengthened.
All FATF and FSRB members must implement the initiatives set out in the FATF Standards and get their implementation rigorously assessed through peer review processes and those of the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank – based on the FATF Common Assessment Methodology.
FATF also produces guidance, best practice documents, and other advice to help countries implement FATF standards. The revision of the recommendations involved extensive consultation and benefited from the comments and suggestions of these stakeholders. The FATF calls on all countries to take effective measures to align their national AML/CFT systems with the revised FATF recommendations.
FATF’s 40 Recommendations
Below is a list of the FATF’s 40 Recommendations broadly classified under 7 categories:
- AML/CFT policies and coordination (Recommendations 1, 2)
- Money laundering and confiscation (Recommendations 3, 4)
- Terrorist financing and financing of proliferation (Recommendations 5-8)
- Preventive measures (Recommendations 9-23)
- Transparency and beneficial ownership of legal persons and arrangements (Recommendations 24, 25)
- Powers and responsibilities of competent authorities and other institutional measures (Recommendations 26-35)
- International Cooperation (Recommendations 36-40)
Therefore, all countries can’t take the same measures to combat these threats. These recommendations thus represent an international standard that countries should implement through measures adapted to their circumstances.
FATF’s 9 Special Recommendations:
The 9 Special Recommendations (also known as Recommendations IX) act in tandem with the 40 Recommendations as a simple framework to aid the detection, prevention, and eradication of terrorism funding.
The 9 Special Recommendations are:
- Ratification and implementation of UN instruments
- Criminalization of terrorist financing and related money laundering
- Freezing and confiscation of terrorist assets
- Reporting of suspicious transactions related to terrorism.
- International cooperation
- Alternative remittance
- Wire transfers
- Non-profit organizations
- Cash couriers
FATF Methods for Assessing Compliance with FATF Recommendations and the Effectiveness of AML/CFT Systems.
To safeguard the financial system against exploitation, the FATF methodology lists 11 essential areas or immediate results that should be attained. The FATF methodology is also used to assess the effectiveness of a country’s actions and whether they meet the technical requirements of FATF recommendations.
The FATF conducts ongoing peer reviews of how its members implement FATF recommendations. These are peer reviews where members from different countries rate another country. An evaluation process will be established to assess compliance with FATF recommendations and the effectiveness of anti-money laundering and anti-money laundering systems.
Assessments emphasize two specific areas: technical compliance and efficiency.
- Performance is the focus of all evaluations. The country must demonstrate that it has an effective framework to protect the financial system against abuse of the risks involved. The evaluation team looks at 11 key areas, or immediate outcomes, to determine the effectiveness of the state’s efforts.
- The assessment also examines whether the country has met all the technical requirements of FATF Recommendations in laws, regulations, and other legal instruments to combat money laundering and terrorism, and the proliferation of weapons of mass destruction.
The peer review report provides a comprehensive description and analysis of the country’s system to prevent criminal abuse of the financial system, as well as recommendations to the country to further strengthen the system.
FATF Compliance with Domain-Centric Approach
The FATF recommendations are the building blocks of an effective framework to combat money laundering and terrorist financing. However, they must be effectively implemented and not simply transposed into national legislation, regulations, or operational frameworks.
The measures must be adapted to the national situation of the country and mitigate the specific risks that the country faces.
Anaptyss as a strategic partner assists banks and financial institutions meet FATF recommendations and regulatory requirements for AML/CFT compliance by leveraging its exclusive Digital Knowledge Operations™ framework and deep-domain expertise in countering finance for terrorism (CFT) and anti-money laundering (AML).
Ensure Compliance with FATF Standards with Anaptyss’s Expert Guidance. Write to us: info@anaptyss.com.