A comprehensive understanding of the risk management lifecycle and risk management strategies is critical to addressing the risks and threats banks and financial institutions encounter throughout their operational lifecycles. Banks need to be agile and proactive in their approach to risk management to make informed decisions and safeguard their assets and reputation.
What is the Risk Management Lifecycle?
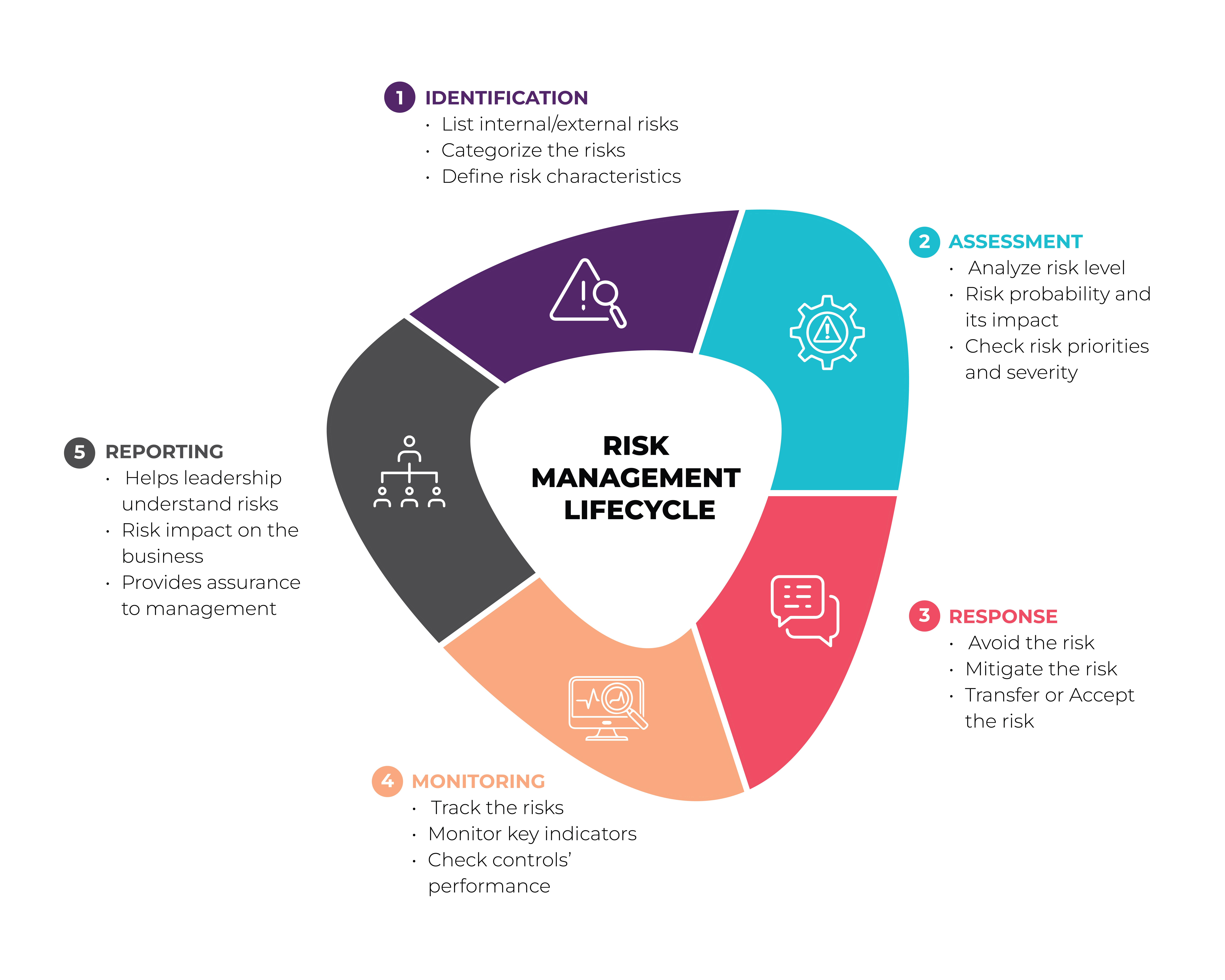
Risk Management Lifecycle is a holistic and structured approach to developing an effective risk management strategy. It is a continuous process that involves risk identification, assessment, mitigation, monitoring, and reporting to ensure that a bank or institution is well-prepared to respond to potential risks and uncertainties in its line of business.
In this blog, we provide a comprehensive overview of the Risk Management Lifecycle for enterprise risk management in the banking industry and discuss the 5 stages of the risk management lifecycle essential to develop an enterprise risk management strategy to effectively identify and mitigate the various business risks.
Stages of Risk Management Lifecycle
The Risk Management Lifecycle in ERM comprises 5 crucial stages to form a continuous risk management process. These include:
1. Risk Identification
Also referred to as risk profiling, it is one of the most crucial steps of the risk management lifecycle that helps banks prepare for potential adverse events and minimize their impact. It involves identifying potential internal and external existing or emerging risks and threats that may obstruct or harm the banks’ or the financial institutions’ strategic goals. Risk identification is accomplished by using techniques such as:
- Brainstorming sessions with stakeholders, employees, executives, and managers
- Interviewing the industry experts and stakeholders
- Reviewing historical data or existing information
- SWOT analysis
- Risk assessment workshops
- Maintain open lines of communication:
- Utilize enterprise risk management frameworks
2. Risk Assessment
After risk identification comes Risk Assessment wherein the identified risks are assessed and analyzed in the following terms:
- Likelihood of occurrence
- The severity level of the risk
- The potential impact on objectives or strategic goals
Risk assessment helps prioritize the resources and attention toward critical risks the bank or financial institution needs to address. Apart from this, the risk management team also formulates various processes for implementing and mitigating risks in the coming risk management lifecycle.
The goal of risk assessment is to:
- Evaluate the hazards
- Determine inherent risks
- Develop a risk profile
- Quantify the risks
- Determine a budget to mitigate the identified risks
- Prioritizing and documenting the risks to the bank’s infrastructure and assets
- Find potential control measures to counter the negative impact of the risks
3. Risk Mitigation
The principle of risk mitigation is to prepare for the risks after evaluating or analyzing the risks and periodizing the plan around the impact. Risk mitigation helps institutions prepare for the worst-case scenarios.
In this stage, the risk management team or the CRO evaluates and implements the risks and risk controls to,
- Bring the risks within the risk appetite of the organization
- Prevent or minimize the likelihood of the risk
- Reduce the impact of the risk on business continuity
This is achieved by providing training and awareness programs for employees and implementing new policies, processes, systems, and controls for mitigating the risks.
We have already discussed the following risk mitigation strategies in another blog:
- Risk Avoidance
- Risk Acceptance
- Risk Transfer
- Risk Monitoring
4. Risk Monitoring
Risk monitoring provides a clear view of the risk landscape based on the line of business. However, it is also a critical and challenging stage of the risk management lifecycle, which involves the risk management team or the CRO evaluating various processes, functions, etc., to identify and monitor the Key Risk Indicators (KRIs) that provide information on the performance of risk controls and mitigation strategies across the organization.
Risk monitoring frequency is often based on the bank and the legal or regulatory requirements. This can be categorized into:
- Voluntary Risk Monitoring: Risk monitoring that is not required by regulatory authorities or law. However, it is part of the risk management plan or strategy.
- Mandatory Risk Monitoring: When the organization is legally bound to monitor risks to meet regulatory compliance and legal obligations such as transaction monitoring to stay compliant with AML/CFT regulations.
The purpose of risk monitoring is to,
- Ensure sufficient risk controls and mitigation strategies to prevent and detect risks
- Having processes to mitigate the effects of risks
- Create transparency across the institutions
- Meet strategic goals by minimizing the risk impact and likelihood
5. Risk Reporting
The last stage of the risk management lifecycle is risk reporting, which involves compiling a complete report on all previously detected and assessed risks that were either mitigated or monitored. This includes frequent risk assessments, control audits, performance evaluations, and consideration of external risk variables that may emerge throughout the next risk management lifecycle.
The goal of risk reporting is to:
- Provide a regular channel for directly informing key stakeholders and upper management
- Ensure that the appropriate information is delivered timely to the persons concerned
- Enhance the banks’ quality of decision-making and strengthen the risk oversight
Conclusion
Effective risk management is essential for organizations to achieve their objectives and safeguard their assets and reputation. To implement a successful Risk Management Lifecycle for effective ERM strategy, banks, and financial institutions need to develop processes to identify, assess, mitigate, and control risks.
As a strategic partner, Anaptyss provides a consultative, data-driven, and tailored approach to banks and other financial institutions in implementing intelligent digital solutions appropriate for the organization’s size, and complexity level. With its exclusive Digital Knowledge Operations™ (DKO™) framework, Anaptyss is helping financial institutions effectively manage critical enterprise risks across all levels.
Want to learn more?
Write to us: info@anaptyss.com

Shahzad Merchant
Associate Director – Enterprise Risk Management

Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *